Understanding DHODH Inhibition
Therapeutic Mechanisms of Action of JBZ-001
On top of the expected nucleotide depletion-induced cell stress, our DHODH inhibitor, JBZ-001, displays multiple mechanisms of action, broadening its potential clinical applications, including:
Explore JBZ-001’s Therapeutic Effects:
Biological Effect
Myeloid Cell Differentiation
JBZ-001 induces the differentiation of immature myeloid cells, driving them toward a more mature, functional state. This is evidenced by morphological changes in AML cells (shown below) and enhanced phagocytic activity in the THP-1 myeloblast cell line, both hallmark indicators of cellular differentiation.
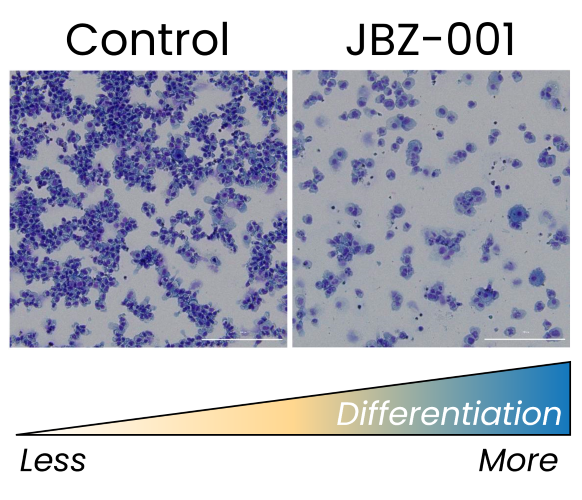
Combination Therapy Potential
Potent Targeted Treatment for Myeloproliferative Disorders like AML
By promoting the differentiation of immature myeloid cells, JBZ-001 holds significant therapeutic potential for treating myeloproliferative disorders such as AML. This mechanism addresses the root cause of these disorders and could improve patient outcomes by restoring normal cell function and reducing disease burden.
To learn more, explore our preclinical data > here.
To learn more, explore our preclinical data > here.

